The purpose of the developed materials is not to eliminate/replace the trainer, but only to enable carrying out classes in an environment close to the real one. A key aspect is to allow training participants to interact with the instructor and other participants in a virtual classroom. For the purposes of the tests, scenes and interactive materials have been prepared, allowing participation in classes based on the Multiuser Telepresence principle.
Open this page on the device which you intend to use for the training participation. Preferably open it in the web browser in your VR device (full functionality). But you can also use a mobile device (full functionality with a user interface designed for touch screens) or a PC Computer (passive participation)
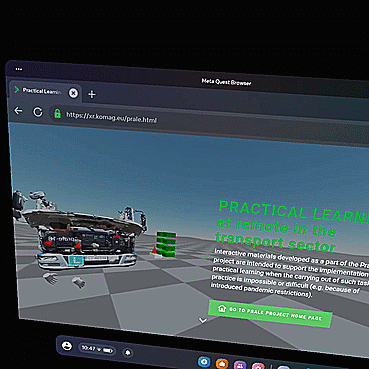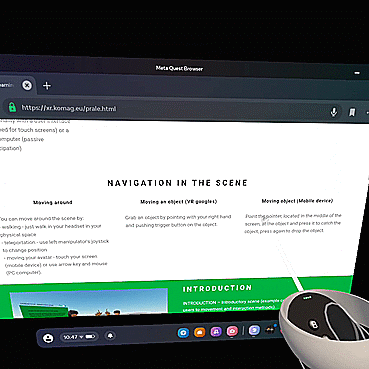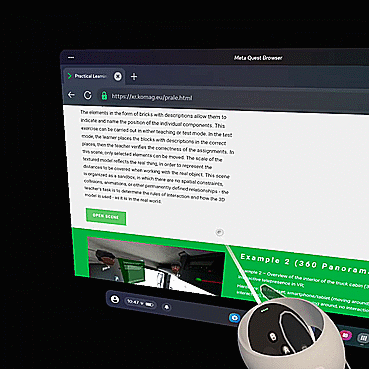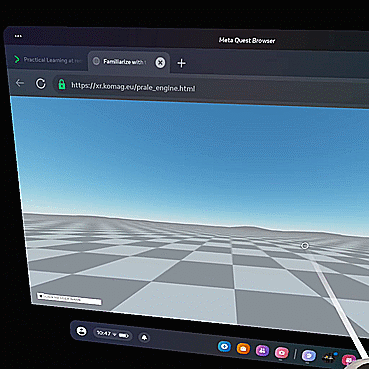
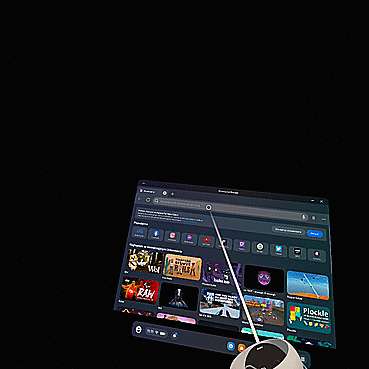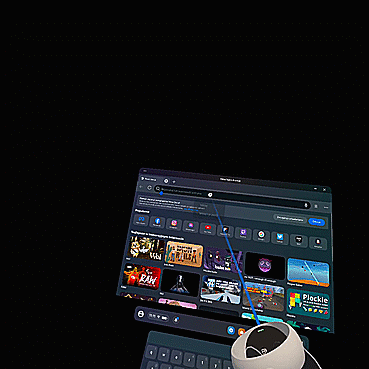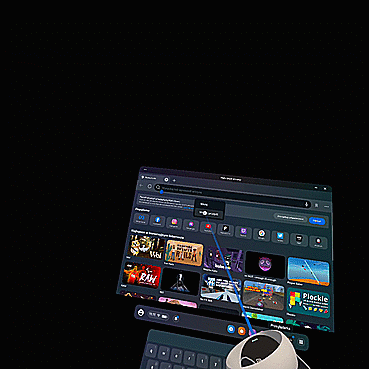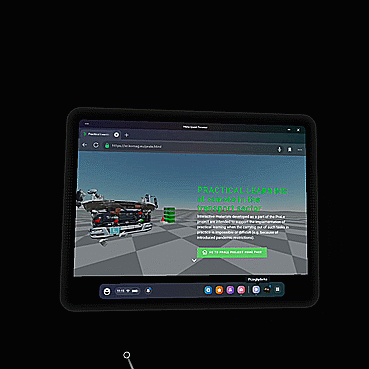
Open exemplary training materials, by clicking "OPEN SCENE". Select the same scene that your trainer has chosen, to meet him/her.
Choose AR (preferably) or VR mode, by clicking available option on the left bottom corner of your screen.
When more than one person attend to the same scene, system automatically presents their avatars in the virtual classroom.

You can move around the scene by:
- walking - just walk in your headset in your physical space
- teleportation - use left manipulator's joystick to change position
- moving your avatar - touch your screen (mobile device) or use arrow key and mouse (PC computer).

Grab an object by pointing with your right hand and pushing trigger button on the object.

Point the pointer, located in the middle of the screen, at the object and press it to catch the object, press again to drop the object.

INTRODUCTION – Introductory scene (example configuration introducing users to movement and interaction methods).
Additional description:
HOW TO INTERACT WITH THE SCENE. In the current version of the solution, everyone has full access to the stage after entering the website address https://xr.komag.eu/prale_start.html.
There are three forms of participation in the lesson:
• passive – a solution for older devices; we can observe the course of the lesson without the possibility of interaction,
• actively on a mobile device – in smartphones and tablets equipped with a depth sensor; after selecting the AR mode, you can freely move around the scene, we catch objects by placing the pointer on the object and touching it, we move the object as intended by moving the screen, with the next touch we leave the object in a specific place,
• full VR interaction – after opening the page in any VR system and switching to AR (with a view of the environment) or VR mode, we can freely move objects with use of manipulators.
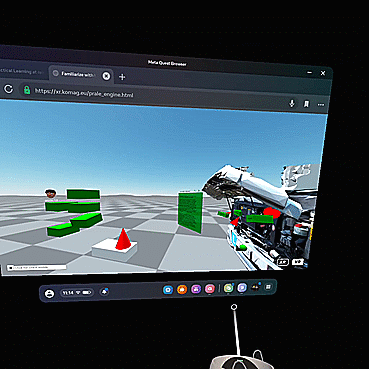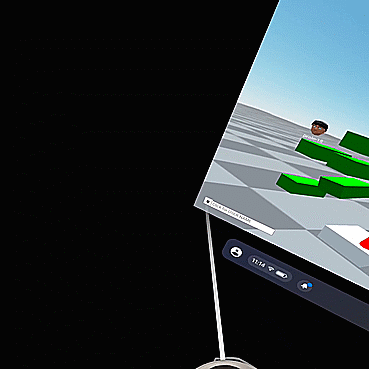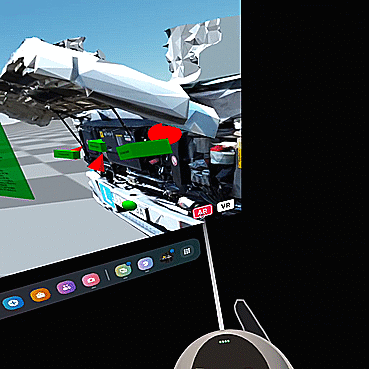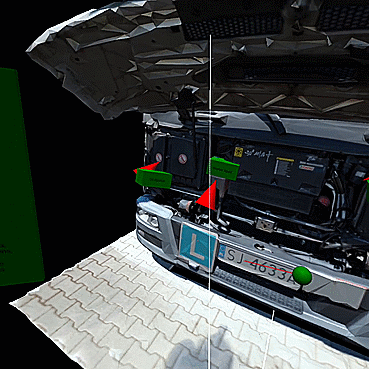
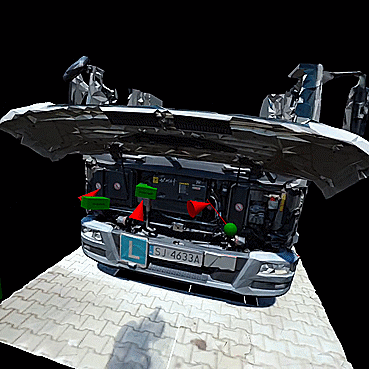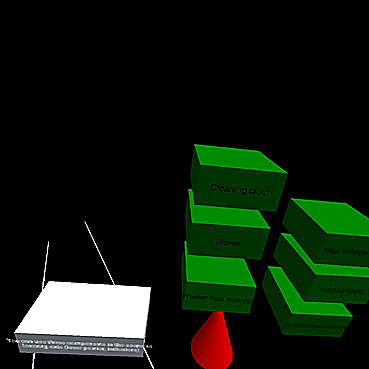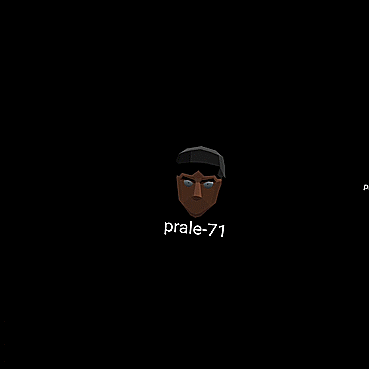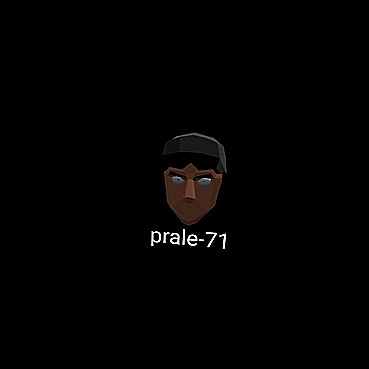
Example 1 – Getting to know the engine compartment of a truck (3D model based on a real object) – Interactive telepresence in VR;
Hardware: VR headset
Additional description:
The purpose of this lesson is to familiarize you with the engine compartment of a truck. The teacher leads the group into the activity's subject and discusses the engine's components. Participants can move freely in the scene and familiarize themselves with its contents. The elements in the form of bricks with descriptions allow them to indicate and name the position of the individual components. This exercise can be carried out in either teaching or test mode. In the test mode, the learner places the blocks with descriptions in the correct places, then the teacher verifies the correctness of the assignments. In this scene, only selected elements can be moved. The scale of the textured model reflects the real thing, in order to represent the distances to be covered when working with the real object. This scene is organized as a sandbox, in which there are no spatial constraints, collisions, animations, or other permanently defined relationships - the teacher's task is to determine the rules of interaction and how the 3D model is used - as it is in the real world.


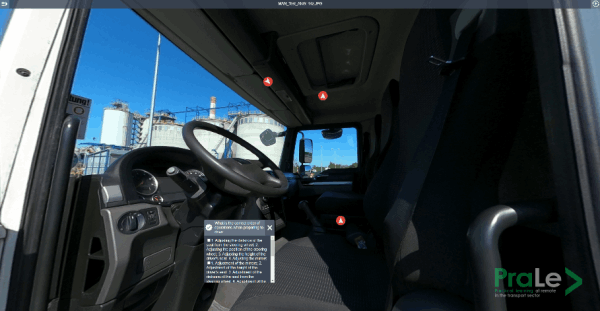
Example 2 – Overview of the interior of the truck cabin (360 photo) – Interactive telepresence in VR;
Hardware: VR headset; smartphone/tablet (moving around, no interaction); computer/laptop (moving around, no interaction)
Additional description:
The purpose of this lesson is to familiarize yourself with typical truck equipment.The trainer, equipped with an indicator, can discuss typical truck equipment, and the group can actively participate in the show. Additionally, it is possible to ask questions and indicate elements that require clarification by the training participants. (In this scene, using a virtual laser pointer, you can indicate the currently discussed elements of the scene).



To reset the scene state, each session participant should close the scene open in the browser (just close the previously opened tab in the browser)
...refresh the page using the F5 key, or reload page on your mobile device.

Truck inspection before driving;
Hadware: computer/laptop, tablet, smartphone, VR headset

Defensive driving (Eco driving) in a truck;
Hadware: komputer/laptop, tablet, smartfon, VR headset

Instructional interactive 360 panorama on vehicle operation and inspection. Hadware: computer, mobile devices (phone, tablet, etc.)
Test interactive 360 panorama of vehicle operation and inspection.
Hadware: computer, mobile devices (phone, tablet, etc.)
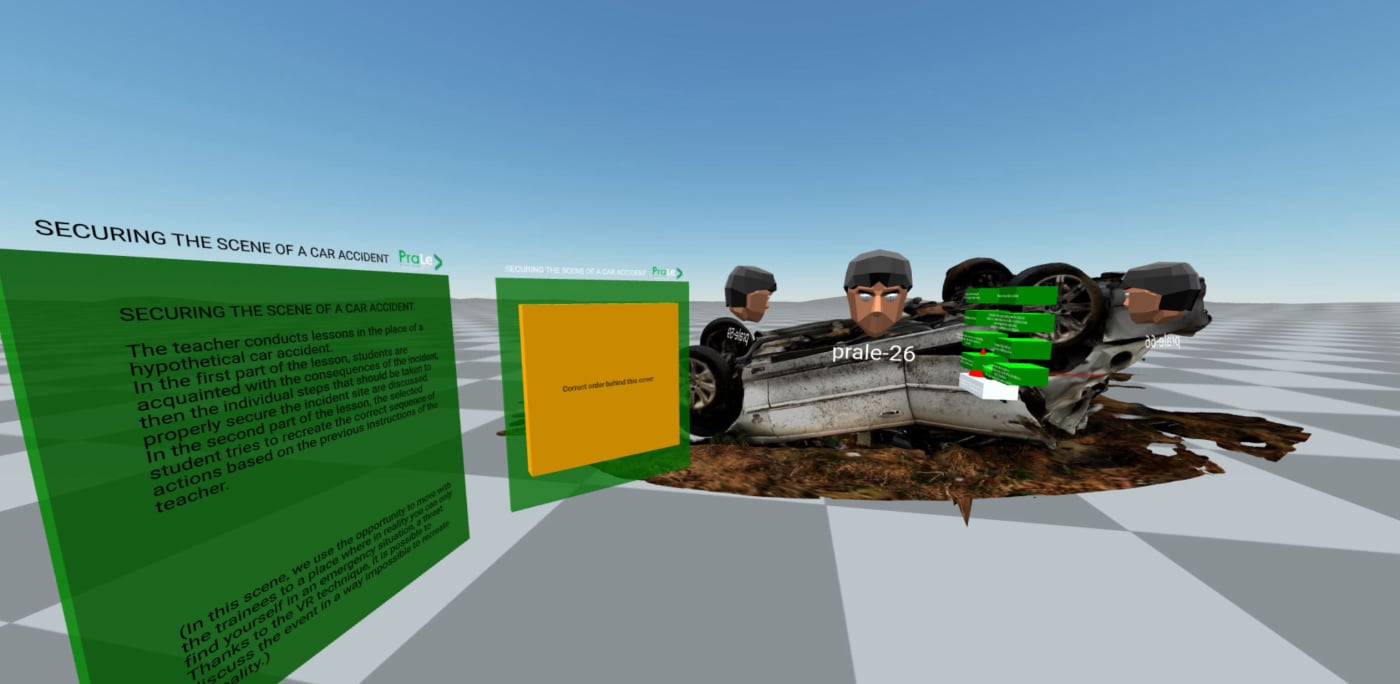
Example 1 – How to behave in the event of an accident (3D model based on a photogrammetry) - Interactive Telepresence in VR;
Hardware: VR headset; smartphone/tablet (moving around, without interaction);
Additional description:
SECURING THE SCENE OF A CAR ACCIDENT. The teacher conducts lessons in the place of a hypothetical car accident. In the first part of the lesson, students become acquainted with the consequences of the accident. Then, the individual steps that should be taken to properly secure the accident site are discussed. In the second part of the lesson, a selected student tries to recreate the correct sequence of actions, based on the previous instructions of the teacher. (In this scene, we use the opportunity to move with the trainees to a place where in reality you can only find yourself in an emergency situation. Thanks to the VR technique, it is possible to discuss the event in a way impossible to recreate in reality.)
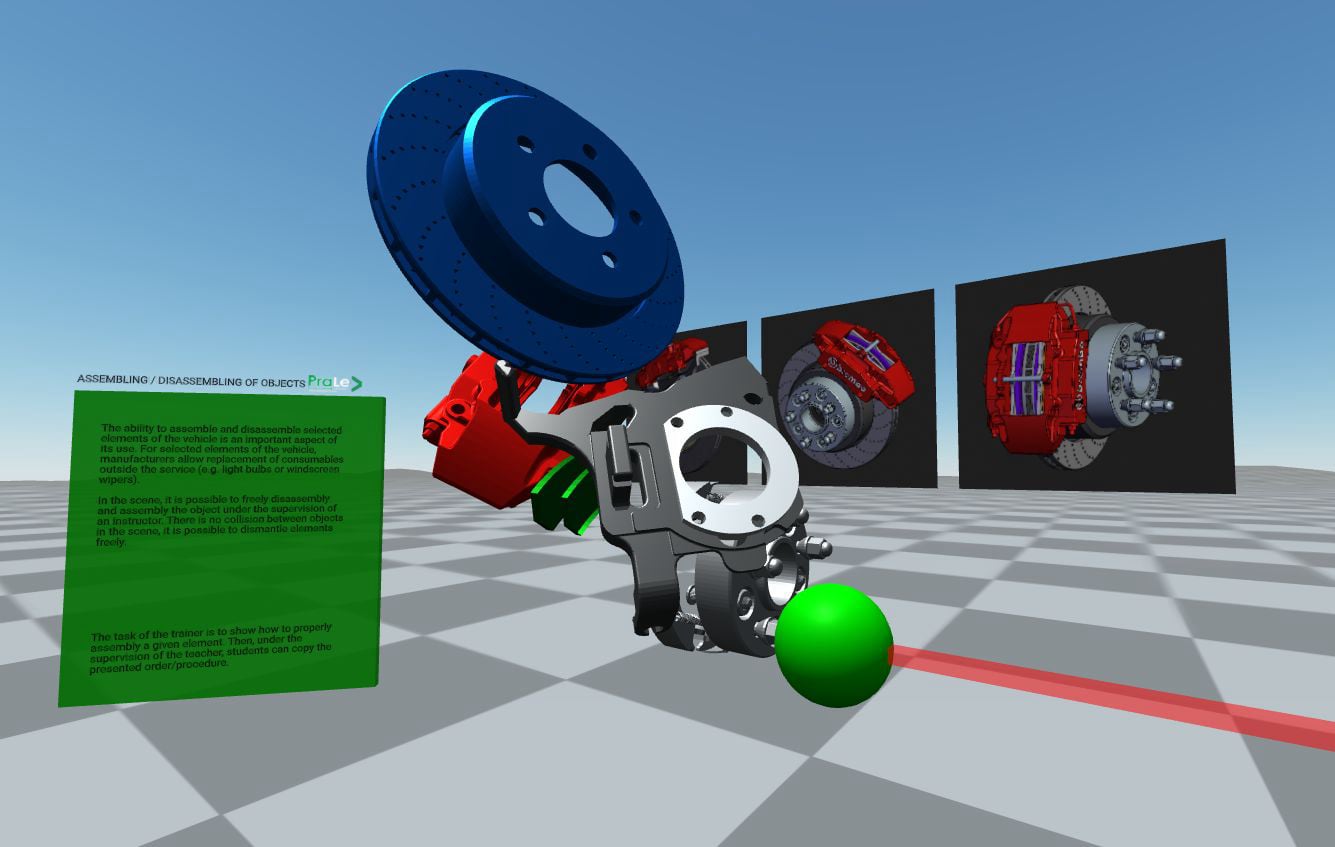
Example 2 – Assembly/disassembly training – Interactive Telepresence in VR; Hardware: VR headset;
Additional description:
The ability to assemble and disassemble selected elements of the vehicle is an important aspect of its use. For selected elements of the vehicle, manufacturers allow replacement of parts outside the service (e.g. light bulbs or windscreen wipers). In the scene, it is possible to freely disassembly and assembly the object under the supervision of an instructor. There is no collision between objects in the scene, it is possible to dismantle elements freely. The task of the trainer is to show how to properly assembly a given element. Then, under the supervision of the teacher, students can copy the presented order/procedure.
Projekt Practical Learning at Remote in the Transport Sector (PraLe) testuje nowe praktyczne metody nauczania i uczenia się dla zawodu transportowca. Testy wykorzystają potencjał technologii cyfrowych w innowacyjny sposób, aby umożliwić naukę na odległość i online.
Copyright © 2023
PraLe ma na celu stworzenie opłacalnego, przyjaznego dla środowiska modelu dostarczania edukacji i szkoleń, który zwiększa efektywność edukacji i uczenia się oraz umożliwia zdalne ćwiczenie praktycznych umiejętności, poprawiając w ten sposób dostęp do edukacji i kwalifikacji dla wszystkich.
Więcej informacji na temat projektu i innych opracowanych wyników można znaleźć tutaj: https://prale.eu/